Sunday, 30 September 2007
Geography Chapter: AgricultureY
Agriculture
As a Primary Industry
-Not only provide food
-also provide raw materials or natural resources that can be used to manufacture products
e.g. harvested grapes used as a raw material for production of wine
Agricultural types/
Forms of agriculture or farming
-Shifting cultivation (Not tested, Oh yeah!)
-Wet Rice cultivation
-Plantation agriculture
-High-tech farming
How they differ?
Purpose of the farm
-farms that produce crops for their own consumption is known as subsistance farming
-while production of crops on a large scale is known as commercial farming
Inputs into the farm
-which include land, labour, materials and capital used by farmers
Produce (outputs) of the farm
-type of crops produced by the farm
Agricultural Types – Wet Rice Cultivation
• It is the growing of rice in flood fields. Rice can also be grown on terraces on hill slopes.
• 90 per cent of the world’s rice is grown in Asia while the other main rice-growing countries are Egypt, Italy, Spain, Brazil and the United States of America.
• Wet rice, or padi, is mostly grown in Asia because the high temperatures and rainfall are suitable for its growth.
Characteristics
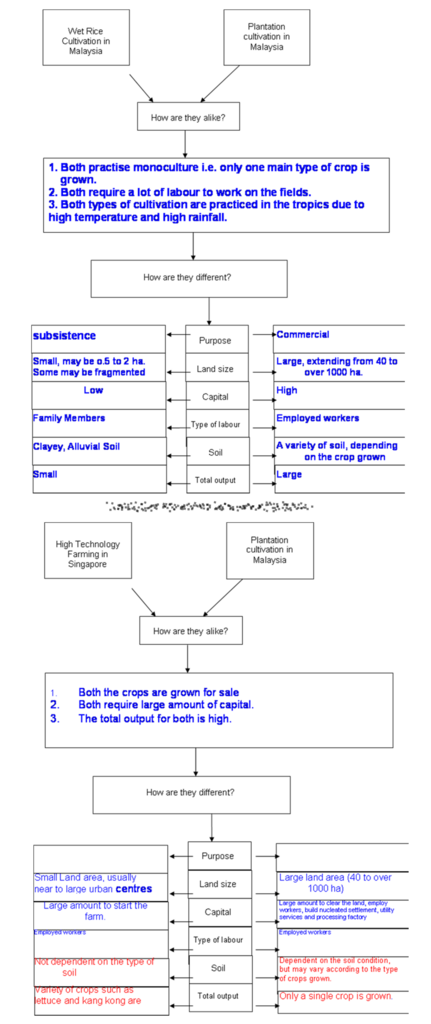
1. Subsistence farmers, mainly for own consumption as it is their staple food.
2. Practice monoculture, growing of one main crop. They may grow vegetables and fruits to supplement their income.
3. Small Size. Varies from half to 2 hectares.
4. Labour intensive because there is a lot of work to be done from ploughing, transplanting of seeds, harvesting, threshing, winnowing and packing. (About 2 ½ times more than the cultivation of other cereals)
5. Level of technology is low for traditional wet rice cultivation.
• It is the growing of rice in flood fields. Rice can also be grown on terraces on hill slopes.
• 90 per cent of the world’s rice is grown in Asia while the other main rice-growing countries are Egypt, Italy, Spain, Brazil and the United States of America.
• Wet rice, or padi, is mostly grown in Asia because the high temperatures and rainfall are suitable for its growth.
Characteristics
1. Subsistence farmers, mainly for own consumption as it is their staple food.
2. Practice monoculture, growing of one main crop. They may grow vegetables and fruits to supplement their income.
3. Small Size. Varies from half to 2 hectares.
4. Labour intensive because there is a lot of work to be done from ploughing, transplanting of seeds, harvesting, threshing, winnowing and packing. (About 2 ½ times more than the cultivation of other cereals)
5. Level of technology is low for traditional wet rice cultivation.
Purpose
-It is practised as a form of subsistence farming as well as commercial farming.
-It is practised as a form of subsistence farming as well as commercial farming.
Inputs
-Land: The size of the farm is generally small. Flat land with clayey soil is most ideal for such farming.
-Capital: It requires higher levels of capital than shifting cultivation. Machinery is used for ploughing and harvesting crops and canals need to be built to irrigate fields.
-Labour: Much labour is required and this comes from either family labour or hired labour. Much of the work such as planting and weeding is usually done by hand. Low walls known as bunds are built to flood the fields. Animals such as water buffaloes may be used to plough the land.
-Land: The size of the farm is generally small. Flat land with clayey soil is most ideal for such farming.
-Capital: It requires higher levels of capital than shifting cultivation. Machinery is used for ploughing and harvesting crops and canals need to be built to irrigate fields.
-Labour: Much labour is required and this comes from either family labour or hired labour. Much of the work such as planting and weeding is usually done by hand. Low walls known as bunds are built to flood the fields. Animals such as water buffaloes may be used to plough the land.
Produce
-High output per unit area.
-Main crop is wet rice.
-High output per unit area.
-Main crop is wet rice.
Agricultural Types – Plantation Agriculture
• It is a form of commercial farming where crops are grown for sale.
• Plantations are found mainly in countries such as Malaysia and India which have tropical climates. These countries usually experience high annual temperatures and receive high annual rainfall.
• Plantation agriculture started in the colonial past in the 18th and early 19th centuries. Most plantations are now owned by local governments or big companies.
Characteristics
1. The crops are grown for sale so they are usually large. Sizes can vary from 40 hectares to over 1000 hectares.
2. It is capital intensive.
3. Modern technology is adopted in the production of crops. The use of high-yielding seeds (HYVs), chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
4. Many plantation crops are perennial crops, with an economic life that extends over many years. Egs such as rubber, oil palm, tea, coffee and cocoa.
5. They are usually grown in neat rows.
• It is a form of commercial farming where crops are grown for sale.
• Plantations are found mainly in countries such as Malaysia and India which have tropical climates. These countries usually experience high annual temperatures and receive high annual rainfall.
• Plantation agriculture started in the colonial past in the 18th and early 19th centuries. Most plantations are now owned by local governments or big companies.
Characteristics
1. The crops are grown for sale so they are usually large. Sizes can vary from 40 hectares to over 1000 hectares.
2. It is capital intensive.
3. Modern technology is adopted in the production of crops. The use of high-yielding seeds (HYVs), chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
4. Many plantation crops are perennial crops, with an economic life that extends over many years. Egs such as rubber, oil palm, tea, coffee and cocoa.
5. They are usually grown in neat rows.
Purpose
-It is a form of commercial farming. Some crops are sold as raw materials to manufacturing industries.
-It is a form of commercial farming. Some crops are sold as raw materials to manufacturing industries.
Inputs
-Land: Plantations take up large areas of land.
-Capital: A large amount of capital is invested in the infrastructure, fertilisers and pesticides.
-Labour: A very large labour force is required to tend to the crops and work in processing factories.
-Land: Plantations take up large areas of land.
-Capital: A large amount of capital is invested in the infrastructure, fertilisers and pesticides.
-Labour: A very large labour force is required to tend to the crops and work in processing factories.
Produce
-Total output is high but its output per unit area is usually low because a plantation covers a wide area of land.
-Usually one main crop is grown. Examples include rubber, coffee, tea, bananas, sugar cane, oil palm, cocoa and tobacco.
-Total output is high but its output per unit area is usually low because a plantation covers a wide area of land.
-Usually one main crop is grown. Examples include rubber, coffee, tea, bananas, sugar cane, oil palm, cocoa and tobacco.
Agricultural Types – High-Tech Farming
• High-tech farming uses modern machinery and farm chemicals to obtain maximum yield from a given plot of land or a group of animals.
• It is practised in countries such as the United States of America, United Kingdom and Singapore.
Fruit and Vegetable Farming
• Crops in a hydroponics farm are cultivated in troughs filled with a nutrient solution and are grown under carefully controlled conditions with the help of computers.
• Plants in an aeroponics farm have their roots suspended in the air, with a nutrient solution being sprayed onto the roots. The air is cooled to simulate conditions found in temperate regions.
Animal Farming
• In cattle farming, cows are housed in special stalls, fed a special diet at exact times and milked by machines daily at appointed times.
• For egg farming in a modern chicken farm, hens are fed a special diet blended by computerised machines, and eggs are collected efficiently by conveyor belts.
Characteristics
1.Large capital is required.
2. Highly skilled labour to carry out research and development to increase crop yield and improve the quality of the output.
3. Less dependent on physical factors. Farmers use soilless culture, tissue culture and the use of computers to automate farm activities.
4. Farms are Intensive to maximize productivity
5. Usually located near large urban centres /cities
• High-tech farming uses modern machinery and farm chemicals to obtain maximum yield from a given plot of land or a group of animals.
• It is practised in countries such as the United States of America, United Kingdom and Singapore.
Fruit and Vegetable Farming
• Crops in a hydroponics farm are cultivated in troughs filled with a nutrient solution and are grown under carefully controlled conditions with the help of computers.
• Plants in an aeroponics farm have their roots suspended in the air, with a nutrient solution being sprayed onto the roots. The air is cooled to simulate conditions found in temperate regions.
Animal Farming
• In cattle farming, cows are housed in special stalls, fed a special diet at exact times and milked by machines daily at appointed times.
• For egg farming in a modern chicken farm, hens are fed a special diet blended by computerised machines, and eggs are collected efficiently by conveyor belts.
Characteristics
1.Large capital is required.
2. Highly skilled labour to carry out research and development to increase crop yield and improve the quality of the output.
3. Less dependent on physical factors. Farmers use soilless culture, tissue culture and the use of computers to automate farm activities.
4. Farms are Intensive to maximize productivity
5. Usually located near large urban centres /cities
Purpose
-It is a type of commercial farming and is important in countries with high population density and limited land area, as it enables maximum output on a small plot of land.
-It is a type of commercial farming and is important in countries with high population density and limited land area, as it enables maximum output on a small plot of land.
Inputs
-Land: Small land area is required as crops are grown closer together.
-Capital: Huge investments are required due to the use of the latest technology, farm chemicals and cost of research and development.
-Labour: The need for human labour is reduced as high-tech farms are highly mechanised.
-Land: Small land area is required as crops are grown closer together.
-Capital: Huge investments are required due to the use of the latest technology, farm chemicals and cost of research and development.
-Labour: The need for human labour is reduced as high-tech farms are highly mechanised.
Produce
-The output per unit area is higher than traditional farming.
-Food such as fruits, vegetables, dairy products and eggs are produced.
-The output per unit area is higher than traditional farming.
-Food such as fruits, vegetables, dairy products and eggs are produced.
. . . . .
know me
littlest of the Pang Family
people call me ChiawMIN or ZhaoMIN
was from Maha Bodhi School
and TanjongKatongSEC
and Temasek Polytechnic
Temasek Design School
tracking people
PANGsters
大哥
二哥
know littlest PUNK even better
HANrelated
MeiFen
MAHA BODHIANS
Alwin
Dennis
LiXin
Michelle
Moyra
TzeChong
YingTing
YingXin
TKsians
Alicia
Amelia
Asha
Atiqah
BoonYee
Celine
Charmaine
Clarissa
Dean
Desiree
Eileen
Erina
EstherTay
EugeneKay
EvelynChan
Farhan NomborSatu
FarisFarizuan
Hafiz
Hasif
HuiMin
HuiJun
HuiXun
James
Janice
JasmineKok
JasminePoh
JiaJun
JinFei
Jolene
Josephine
JovanYo
JunHui
Kane
Kenneth
Mark
Michelle
MingJie
Nazri
NicholasAw
Nigel
Nikki
Novia
PohKing
Rifat
Rohaida
Ryan
SandyLikitdachavongs
Sara
Sharmane
Sharon
SiHui
SiYan
SiYuan
SooHan
Stefan
WeiLin
WeiYing
YinShuang
YongJia
Xenia
Yuyi
ZhangXin
NgeeAnnSec
ChinaExchange'07
Pamela
SherylChia
Shimei
TzeChong
ZhongHuaSec
ChinaExchange'07
ChiehLing
Grace
Stella
them
TK3J'08cum4J'09
Crystal
KelvinPang
WeiYing
YanYing aka YY
YeeJia
YuJia
other STUDENT LEADERS
JonothanSeng/HwaChongInsttn
JoelLim/MarisStella
ShaunSeah/MarisStella
Jesmine/TKGS
CherylSeah/PLMGSS
EleanorNeo/PLMGSS
Hannah/PLMGSS
Joanne/PLMGSS
WeiKee/PLMGSS
ZiQi/PLMGSS
yellowed pages
September 2007
October 2007
November 2007
December 2007
January 2008
February 2008
March 2008
April 2008
May 2008
June 2008
July 2008
August 2008
September 2008
October 2008
November 2008
January 2009
February 2009
March 2009
April 2009
May 2009
June 2009
July 2009
August 2009
September 2009
November 2009
December 2009
January 2010
February 2010
March 2010
April 2010
May 2010
June 2010
July 2010
August 2010
September 2010
October 2010
November 2010
January 2011
February 2011
June 2011
July 2011
CREDITS
Layout - Novemrain
Hosting - Blogger
Image - DeviantArt