Geography Chapter: Transport and CommunicationsY
Types of Transport
Land
-Trains
-Cars
-Bicycles
Water
-Ships
-Ferries
-Canoes
Air
-Spacecraft
-Aeroplanes
-Helicopters
Transport Hub
-countries or cities with a variety of well-connected transport networks or system
-people from all over the world get to these places easily
-people can mive around easily in these places
-these places are very well-connected
E.g. London
-5 airports, 6 railway terminals, well-connected roads, may also travel by water
-extensice public transport system; buses and trains running on land and underground
-one of the world's busiest airports, welcoming more than 11 million international visitors each year
Types of Communications
Print Media
-printed format such as newspaper and magazines
Telecommunications
-send signals and messages over long distances using electronic equipment like radio, TV, telephone, the Internet
-satellite television : allowing people to view live events taking place in other countries
Effects of development (or rather, technological advancement)
Increased accessibility
-able to travel longer distances within a shorter period os time
-able to move goods faster, and in greater amounts, than ever before
E.g. England and France being seperated by English Channel
the Channel Tunnel was then built in 1994 under the waters, across the English Channel to increase the accessibility between Englad and France
Increased connectivity
-able to exchange information and trade with people who live in distant places more easily
-good communications network can benefit and enhance transport system (like how pilots maintain close contact with airports to ensure a safe journey)
Shrinking World
-world have seems to have shrinked due to technological advancement
-faster to travel between places
-faster to communicate with one another
-faster in obtaining information from other parts of the world
-business can be carried out across countries with greater ease
-helped in developing a culture of entrepreneurship
Globalisation
-spreading of information, ideas, cultures and value from one place to another easily
Case Study: Singapore
Why a transport and communications hub
Well-positioned at the centre of international transport routes
-attracting traders around the world
-led to development of services like transport, communications, warehousing and processing industries
How can being a transport and communications hub help us earn money?
Increasing demand for goods and services
-when more ships stop at our ports, demand for related services like ship repair
Attracting overseas companies to set up business
-well-developed transport and communications network makes it convenient to contact with other companies faster and easier
-hence attracting foreign companies to locate business here, creating job opportunities for locals
Increasing opportunities for doing business overseas
-greater connectivity encourages local companies to seek opportunities overseas
E.g. with the use of the Internet, local businessmen can communicate with foreign businessmen without travelling to meet face to face
Singapore as a Transport Hub
Air
-upgrading of airport to cope with increasing number of passengers
-T1, T2, Budget Terminal, (and up coming T3)
-serving over 80 airlines flying to more than 50 countries
-handling 44 million passengers per year
-by 2008 (completion of T3), can cater to over 64 million passengers
Sea
-one of the busiest ports in the world
-operated by PSA International and Jurong Port
-well-connected with 200 shipping lines to 123 countries
Land
-advanced network of roads, expressways and railway lines
-4 main espresswasy, 2 train systems (MRT & LRT), buses and taxis
-transportation system provides access to ports and airports, connecting people to the rest of the world
-road and railway connected to Malaysia
Singapore as a Communications Hub
Mass media
-encourage international media companies to set up here
-hence encouraging growth of local media companies
Information Communications Technology (ICT)
-develops new IT products like softwares
-softwares to help keep track of business deals and customer information
-government encourage use of the Internet for education, business and recreation
-meanwhile, developing a culture of entrepreneurship
. . . . .
Geography Chapter: AgricultureY
• It is the growing of rice in flood fields. Rice can also be grown on terraces on hill slopes.
• 90 per cent of the world’s rice is grown in Asia while the other main rice-growing countries are Egypt, Italy, Spain, Brazil and the United States of America.
• Wet rice, or padi, is mostly grown in Asia because the high temperatures and rainfall are suitable for its growth.
Characteristics
1. Subsistence farmers, mainly for own consumption as it is their staple food.
2. Practice monoculture, growing of one main crop. They may grow vegetables and fruits to supplement their income.
3. Small Size. Varies from half to 2 hectares.
4. Labour intensive because there is a lot of work to be done from ploughing, transplanting of seeds, harvesting, threshing, winnowing and packing. (About 2 ½ times more than the cultivation of other cereals)
5. Level of technology is low for traditional wet rice cultivation.
-It is practised as a form of subsistence farming as well as commercial farming.
-Land: The size of the farm is generally small. Flat land with clayey soil is most ideal for such farming.
-Capital: It requires higher levels of capital than shifting cultivation. Machinery is used for ploughing and harvesting crops and canals need to be built to irrigate fields.
-Labour: Much labour is required and this comes from either family labour or hired labour. Much of the work such as planting and weeding is usually done by hand. Low walls known as bunds are built to flood the fields. Animals such as water buffaloes may be used to plough the land.
-High output per unit area.
-Main crop is wet rice.
• It is a form of commercial farming where crops are grown for sale.
• Plantations are found mainly in countries such as Malaysia and India which have tropical climates. These countries usually experience high annual temperatures and receive high annual rainfall.
• Plantation agriculture started in the colonial past in the 18th and early 19th centuries. Most plantations are now owned by local governments or big companies.
Characteristics
1. The crops are grown for sale so they are usually large. Sizes can vary from 40 hectares to over 1000 hectares.
2. It is capital intensive.
3. Modern technology is adopted in the production of crops. The use of high-yielding seeds (HYVs), chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
4. Many plantation crops are perennial crops, with an economic life that extends over many years. Egs such as rubber, oil palm, tea, coffee and cocoa.
5. They are usually grown in neat rows.
-It is a form of commercial farming. Some crops are sold as raw materials to manufacturing industries.
-Land: Plantations take up large areas of land.
-Capital: A large amount of capital is invested in the infrastructure, fertilisers and pesticides.
-Labour: A very large labour force is required to tend to the crops and work in processing factories.
-Total output is high but its output per unit area is usually low because a plantation covers a wide area of land.
-Usually one main crop is grown. Examples include rubber, coffee, tea, bananas, sugar cane, oil palm, cocoa and tobacco.
• High-tech farming uses modern machinery and farm chemicals to obtain maximum yield from a given plot of land or a group of animals.
• It is practised in countries such as the United States of America, United Kingdom and Singapore.
Fruit and Vegetable Farming
• Crops in a hydroponics farm are cultivated in troughs filled with a nutrient solution and are grown under carefully controlled conditions with the help of computers.
• Plants in an aeroponics farm have their roots suspended in the air, with a nutrient solution being sprayed onto the roots. The air is cooled to simulate conditions found in temperate regions.
Animal Farming
• In cattle farming, cows are housed in special stalls, fed a special diet at exact times and milked by machines daily at appointed times.
• For egg farming in a modern chicken farm, hens are fed a special diet blended by computerised machines, and eggs are collected efficiently by conveyor belts.
Characteristics
1.Large capital is required.
2. Highly skilled labour to carry out research and development to increase crop yield and improve the quality of the output.
3. Less dependent on physical factors. Farmers use soilless culture, tissue culture and the use of computers to automate farm activities.
4. Farms are Intensive to maximize productivity
5. Usually located near large urban centres /cities
-It is a type of commercial farming and is important in countries with high population density and limited land area, as it enables maximum output on a small plot of land.
-Land: Small land area is required as crops are grown closer together.
-Capital: Huge investments are required due to the use of the latest technology, farm chemicals and cost of research and development.
-Labour: The need for human labour is reduced as high-tech farms are highly mechanised.
-The output per unit area is higher than traditional farming.
-Food such as fruits, vegetables, dairy products and eggs are produced.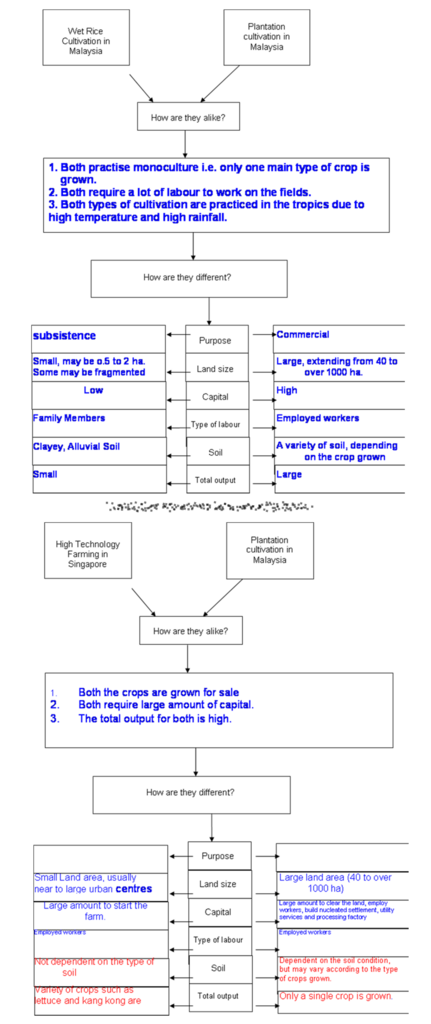
. . . . .
Saturday, 29 September 2007
Geography Chapter: SettlementsY
Settlement patterns
 Nucleated
Nucleated-buildings are clustered together
-in a compact area
-which is usually the meeting point of transport routes
 Linear
Linear-buildings are neatly lined
-located along main transport routes such as roads, railways, rivers and canals.
 Dispersed
Dispersed-individual buildings are scattered
-over a wide area
URBAN SETTLEMENT
Poplulation size and density
-large population size
-activities are concentrated in an area, hence settlements are built close together
-population density is high
Main function
-manufacturing
-business
-commercial
-administrative (government)
Amenities
-many shops offering a wide range of goods and services
-wide range of facilities, including a dense transport network of roads and railway line
Way of life
-people work to serve other people rather than produce food to meet their own needs
-higher level of income
-livelihood of people does not depend as much on the physical environment as compared to a rural settlement
RURAL SETTLEMENT
Population size and density
-small population size
-settlements are dispersed over a large area
-population density is low
Main function
-fishing
-mining
-farming
-forestry
Amenities
-provides basic necessities and facilities (goods and service)
Way of life
-people work to meet their basic needs
-livelihood of the people depends on the physical factors
DEFINITIONS
Rural settlement: A settlement where the majority of the people are involved in activities such as manufacturign and business. Population size is often large and population density is low.
Urban settlement: A city or town where the majority of the people are involved in activities such as manufacturing and business. Population size is often large and population density is high
. . . . .
Friday, 28 September 2007
Geography Chapter: PopulationY
Low rate of population growth
Causes: -Low Death Rate -Low Birth Rate
Factors leading to Low Death Rate:
1. High standards of hygiene
-less prone to diseases associated with unhygienic living conditions (e.g. cholera)
2. Higher levels of income
-people are able to afford better nutrition and do not suffer from food shortages
3. Better medical and health care
-improve the survival rate of babies, redicing infant mortality rate
-less prone to falling sick
-less prone to contracting diseases due to better hygiene and clean living conditions
Factors leading to Low Birth Rate:
1. Late marriages
-couples tend to have fewer children because they have fewer years to have babies
2. Fewer marriages
-result in fewer families and fall in birth rate
3. Preference to have smaller families
-due to increase in cost of living and raising kids
-and difficulties in balancing work and family life
Consequences of Low rate of population growth
1. Ageing population
-increase in burden on the working population as there are mroe elderly joining the workforce and fewer youths
2. Higher taxes
-each working person has to pay more tax to fund public amenities and projects
3. Smaller talent pool
-fewer people to choose from to lead and serve the country
Actions to manage Low rate of population growth
1. Encouraging marriange and childbearing
-gives incentives in the form of tax rebates to couples who have more children (e.g. Singapore)
2. Need of an ageing population
-building special facilities for elderly and encouraging their families to care for them
3. Special facilities
-specialised hospitals to treat illnesses associated with the elderly and homes catering to them
4. Keep elderly healthy and active
-opening exercise classes and courses for lifelong learning at community centres
5. Extend working life
-to reduce the burden on the working population
-to raise retirement age
6. Encourage financial planning
-early planning to ensure people have enough financial resources when they retire to meet their life goals
High rate of population growth
Causes: -Low Death Rate - High Birth Rate
Factors leading to Low Death Rate:
1. Better medical and health care
-improve the survival rate of babies, reducing infant mortality rate
-less prone to falling sick
-less prone to contracting diseases due to better hygiene and clean living conditions
Factors leading to High Birth Rate:
1. Lack of family planning
-common in less developed countries
-less educated and unaware of family planning methods
2. Early marriages
-increase childbearing years for the women
3. Preference for sons
-parents have children till they succeed in having sons (e.g. China and India)
4. Need for farm labour
-common in less developed countries
-large families to provide more hands to work in the fields
Consequences of High rate of population growth
1. Demand for resourses
-food and water increases with more people
-less developed countries often suffer from the shortage of food due to insufficient production of food
2. Higher demand for housing
-demand for housing increases with more people
-inadequate housing for growing populations in cities of less developed countries
3. Lack of proper housing
-squatter settlements and make-shift houses have sprouted around the outskirts of cities of less developed countries
4. Rapid population growth
-leading to intense competition for limited number of jobs
5. Environmental problems
-lack of proper waste disposal services to deal with the waste produced by the people
-waste left unattended to can lead to pollution of the environment and the deterrioration of living conditions
Actions to control a High rate of population growth
1. Education
-proper family planning methods can teach couples to control the size of their families
2. Incentives and penalties
-tax subsidies may be given to couples who have fewer children while those who have more may be punished with higher taxes
EXAMPLE: CHINA'S 'ONE CHILD POLICY'
fine couples who have more than one child while providing education and housing subsidies to those who complied with the policy
Definitions:
- Infant Mortality rate: the number of deaths among infants under one year of age for over 1000 live births per year
- Life Expectancy: the average number of years a person living in a particular area is expected to live
- Rate of Natural Increase:
Birth Rate - Death Rate = Rate of Natural Increase
. . . . .
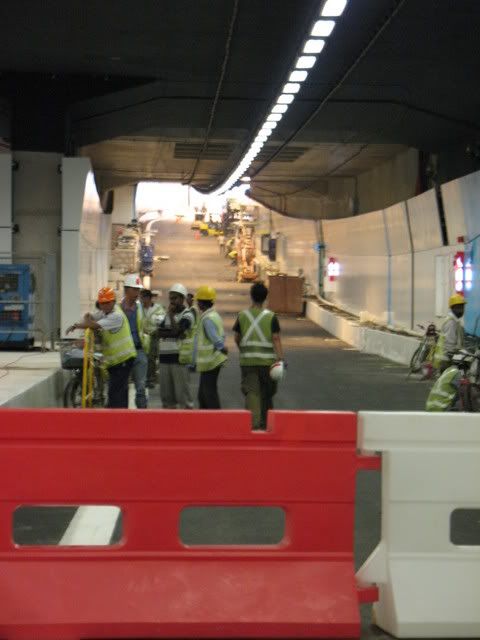
Yesterday, I went to the newest expressway in Singapore, the KPE (Kallang-Paya Lebar Expressway). It's a underground tunnel connecting from the ECP (East Coast Parkway), crossing under Pelton Canal, Paya Lebar Road, Airport Road, emerging at ground level at Defu Lane, and joining TPE (Tampines Expressway) at Lorong Halus. This major project was planned way before I was born, in the 1960s, and cost S$1.8 billion! The design is nice, safety precautions are also well taken care of, and the ventilation system is ultra cool! Well, I think LTA(Land Transport Authority) had done a remarkable job in conservation for the environment, by land preservation, preserved field truck, minimized surface disruption, and reducing noise and dust pollution. More picture in the tunnel: For more information on KPE, check out: http://www.kpeunderground.sg/ And if you're interested, you can join LTA for the Family Day cum Walk-a-Jog at KPE on Sunday, 21 October, 7.30am to 2pm. You'll get to run on the tracks before the vehicles do!!!
KPE pre-opening exhibitionY
Just look at this video on how we've all enjoyed ourselves when all 3 of the Saccardo nozzled were switched on:
Guess what is the speed of air through that air-sock-like thing? Believe it or not, it's 30metres/sec! The KPE Tunnel Discovery begins...
The KPE Tunnel Discovery begins...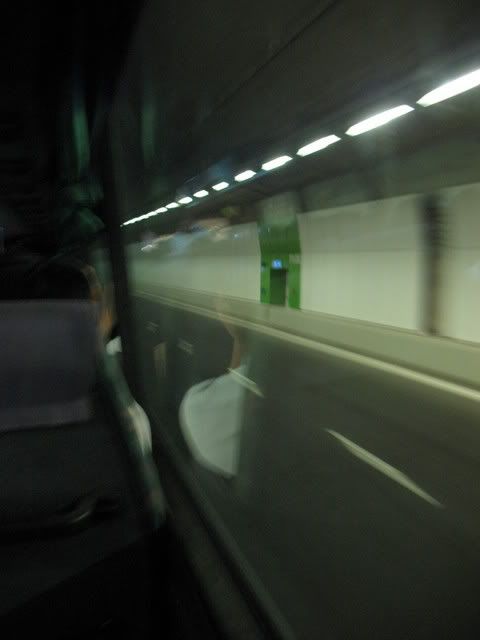 Travelling through the completed part of the underground tunnel...
Travelling through the completed part of the underground tunnel...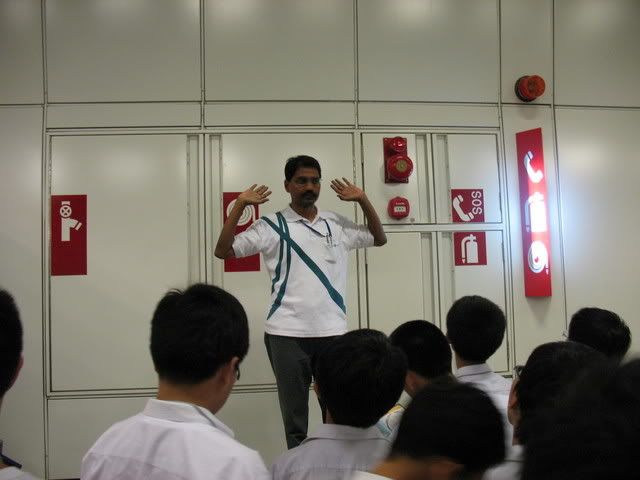
Check out the emergency cabinet! It has everything you need during an emergency! Travelling up the emergency escape staircase...
Travelling up the emergency escape staircase... Coming out of the escape staircase... so we were under this place all this while!
Coming out of the escape staircase... so we were under this place all this while!
Gosh, we were captured by the surveilance camera in the tunnel! (twist to the camera... michelle!)
That's the Saccardo nozzle. Only 1 at full blast.
2G girls who went... Sharmane, Eileen, Michelle, Astrid, Me
Mrs Tan's Geography classes: 2C, 2G, 2H (TK group 2)
Try this game too: https://www.transport2020.gov.sg/
. . . . .
Tuesday, 25 September 2007
Mid-Autumn FestivalY
一口月饼 一口茶
赏着明月 饮茶香
全家大小 聚集啦
八月十五 那一晚
点上灯笼 照明夜
许个小愿 保平安
温情夜晚 人人亨
中秋节是个家庭团聚的好日子; 如果真的赶不急到家,至少和家人通个电话报平安.
今年的中秋节与往年的差不多... 最喜欢的仍然是各种类的茶及冰皮月饼!!!

在此祝贺大家中秋节愉快!
. . . . .
Sunday, 23 September 2007
Make me understand whyY
I told my brother that and he said he needed to use the computer too. He suggested that I print whatever I needed to copy from, but I felt that it was really a waste of resources ( papers, ink, time). He said it would be faster, I would not even have to copy.
I reiterated that I had to write things out to better understand. Guess what, he asked me to print it out then write out -.-
"Forget it," I uttered, and took all my stuff and went back to my room, thinking of just letting him use the computer, I could always go back when nobody's at home.
And guess what (again), he came over to my room and told me a whole lot of nonsense:
-that he gave suggestions and I didn't even bother
-that by saying "forget it", I'm showing him that I had no interest for Geography
-that if I were to use the computer, it would be affecting his time
I didn't want to argue, so I ust moved on with Literature first. Since me studying would affect him, whatever he had to use the computer for must have been urgent.
*NOTE: I was an A1 student for physical geography; I love the environment (don't believe? You can ask Yuyi or Clarissa, I have been emphasizing on being green), and Geography is 1 important factor in life, how would I ever lost interest in it?!?!
Anyway, after about 20 minutes analysing the story Durian, I went for a toilet break, passing by 大哥's room (where the computer is). Guess what (again) was on the screen of the monitor? Motion graphics, Anime! At that moment, I really had nothing to say. No point argueing or getting on fire.
Hey brother, you have your own laptop, so why fight over the computer with me when I'm using it for serious studying???
. . . . .
Thursday, 20 September 2007
Counsillors have more privileges? even shown by our badges?Y
"Silver," was the response from the class. Mrs Ang seemed to have a big question mark on her head.
Then about 1 second later, Siddharth mumbled, "Errr... gold?!" The question mark on Mrs Ang's head changed into a lighted bulb immediately!
I looked at the back of my council badge too, it was GOLDEN IN COLOUR!
"Hey, counsillors big arh?!?! Counsillor badge golden eh, how come arh???" came a voice from the back.
Mrs Ang grinned, then continued on with her lesson. "Only the counsillors' badges are golden behind, because the metal used had been electroplated." And she went on to the process and how electroplating actually works. Hmmm... tomorrow we'll be doing the practical experiment on it, guess it'll be lots of fun!
Anyway, I'm still wondering why's the back of our badges golden unlike the normal scholl badge which is silver. Probably because of our status, but not to forget, with great power comes great responsibility.
. . . . .
Monday, 17 September 2007
PHONE!!!Y
But I still can't forgive myself for relying so much on that stupid brown bag which is NOT considered a bag if the 2 knots come loose and they always do! Anyway, I don't feel empty as I'm not a super techie whom will die without a phone, so Life still goes on and I just learnt my lesson.
I don't think anyone who picked up that phone will want it since it's really old-biang and not very good looking. To me, it's still the dearest phone as it was my first mobile phone and guess what, I even styled it with fanciful tapes to accessories it! Sometimes when I see old uncles and aunties carrying the same model, I feel kind of in as my phone though having cracks here and there looks better and chio-er... haha...
Anyway, tar tar to my dearest and I'll be extra careful handling my valuables next time and I SWEAR I'M SO GOING TO THROW AWAY THAT USELESS BROWN BAG!!!
. . . . .
Friday, 14 September 2007
Happy Birthday, MumY
When we walked into the restaurant, just passing the dessert counter alone was satisfying enough! The place had a very cosy kind of European style, with a lot of European architecture details. Moreover, the lighting and the background music was set at the perfect tone. It was just nothing but heavenly to be able to enjoy such a sweet and romantic evening!
some pictures:
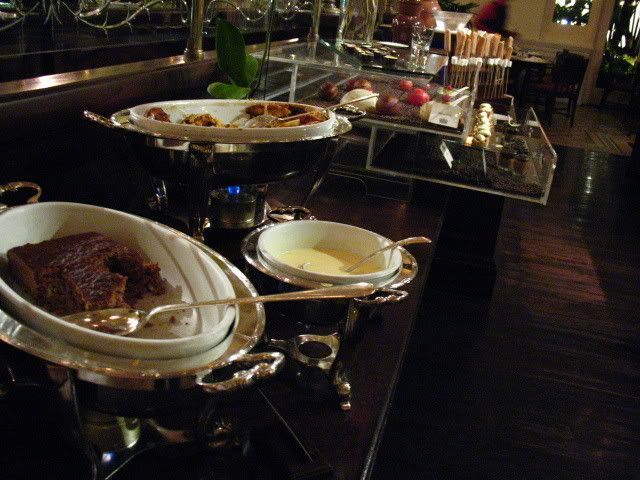
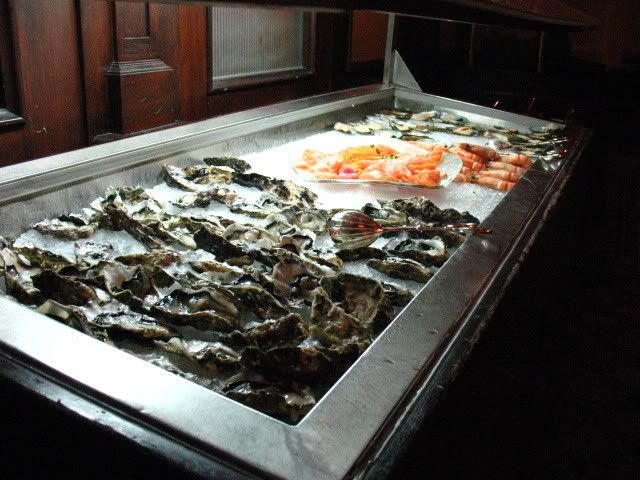
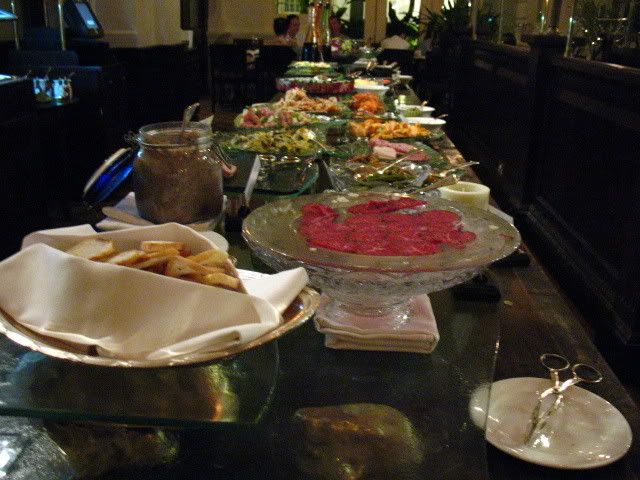




check out more pictures on my friendster here
. . . . .
Monday, 10 September 2007
short hairY
二哥was laughing at it the whole time, saying that he's having a younger brother. He said I looked totally like a BOY from the back and that I should get myself a pair of shorts to school tomorrow.
Okay, guess I shall have to make the best out of it and wait for my hair to GROW...
. . . . .
Thursday, 6 September 2007
Human TetrisY
. . . . .
Refreshing MINtY
This is what you watch on local TV stations in Southeast Asia:
This is from some foreign country:
This one is super disgusting and can be quite offenssive:
This is the anime version, kind of no link:
These are the various versions found in India:
. . . . .
Monday, 3 September 2007
Youth ProblemsY
-cyber wellness
-gangs
-theft
-school bullying
what would be the first thoughts that come to your mind?
Well, to be honest, our mission for Youth Congress 2007-2008 is to try our best to help others walk away from the negative route and be a positive influence. But what are these 4 key issues really about? Why is the National Youth Council bringing these up?
Cyber Wellness
Think about it, is pushing that power button of the CPU the first thing you do when you head home? Do you spend more than 10 hours a day on the computer?
People often have the wrong impression of cyber wellness, thinking that if he/she is not a gamer, he/she can simply neglect it. Cyber wellness is not just about the effect of gaming, it has got to do with anything that has got to be related to using a computer. Educators emphasize more on gaming mainly because the the severity of the consequences is getting worse and that gaming has become so much more common world wide that it has already become part of many's everyday routine.
Gaming is not something bad, it serves us as a form of entertainment and may also help us get to know our peers even better through team games and we may also pick up some thinking skills through strategic games. However, overplaying may result in addicttion or not facing reality life. They're people who just go on playing without sleeping for days, and feeding themselves with instant noodles, or can't even bear to leave the computer just to ease their bladder! I can only describe these group of people as a group of a group of pathetic addicts with totally no life! Seriously, life is much much more than just living in your virtual world and being powerful in your game.
Not only will you start to neglect your studies, you'll slowly drift away from reality, ignoring the people around you, eventually forgetting that you're a human being and that you need to take care of yourself (not your avatar/character) and stay healthy and socialise with people.
Gangs
Youth join gangs mainly because they themselves were once a victim of bullying, have social conflicts and seek for protection, it is an easy way to get money and seek fun, they feel proud or powerful being part of a gang. Gangsters believe strongly in loyalty towards their gang leader and "brothers". We all know that gangsters are up to no good, never once bringing peace, neatness or smiles to us. Nevertheless, there are points where we can learn from them : loyalty, sense of belonging, having status (recognition), short-run hedonism, versatility; it's just whether or not we're over doing these, creating chaos and havoc (or what gangsters like best, malice and negativism).
Here's a little test to see if you're walking a step closer to joining a gang:
1) Life is interesting, exciting and relaxing in a youth gang, whereas life is boring, tedious with too much pressure from examinations as a school youth.
2)As a gangster, I learn from actual life experiences and my life scope is wide. In school, subjects studied are impractical and disconnected with daily life.
3)In a youth gang, I'm being protected and I feel secure. But if I'm only a school youth, I'm terrorised by gang members.
4)Being a gangster, I'm not controlled and have lots of freedom, whereas being a school youth, there're too many regulations and life is controlled.
5)If I'm in a youth gang, I have authority over others. I take the decision making power into my own hands. A school youth has no authority at all. The adults always make the final decision and I have to obey.
6)Gang life is versatile and attractive, I feel the sense of belonging. I do not identify with school, schooling is just a daily routine.
7)Living in a small commune, we share our money and partners, fight and work together. In school, I'm being trained to be individualistic, people are classified into ranks, not by ability but by paper qualifications.
8)In a youth gang, there's a diversity of recognition, with accompanying praise, respect and accpetance. I have this sense of achievement. Whereas in school, academic achievement is the main concern, it's totally a sense of failure.
9)Hedonism is the goal of this materialistic world. Quitting school earlier to start earning money should be the way of life. There's no hope for the future even if I complete secondary school.
Every YES I AGREE to any of the following above, you've got to be extra careful as you're seriously in danger of getting into a youth gang.
Theft
When we're talking about theft, we're actually discussing it as a general topic. Theft can be scrolled down into theft (just stealing in any occassions), shop theft and robbery. There are also related offences such as retaining stolen properties and helping other parties in the act of stealing.
Do you know the consequences one has to face for the various acts?
THEFT: 3 years imprisonment, fine or both.
SHOP THEFT: 7 years imprisonment, fine or both.
ROBBERY: 2-10 years imprisonment, with at least 6 strokes of the cane (depending on the severity of the act)
Despite the painful consequences, many youth still break the law. The theft and other related offences accounted for 61% of the overall crime reported in 2006 (20 519 cases). There are a total of 3645 youths arrested for crime in 2006 (19% of total persons arrested by the Police). And the most common offences committed by youths are SHOP THEFT, THEFT AND RIOTING.
But why? why? why? why do these people still steal??? I believe many of us have the answer to it. Living in this cosumer's world, everything os money. People get desperate for money, lazy ones want easy money, etc., etc., the list just goes on.
1 very intersting way i learnt to help anyone to get that itch of stealing is to remember the traffic light : RED, AMBER, GREEN. Before getting your hands on to anything you're interested in taking, stop. Think through thoroughly; think about how by taking someone else's belongings will affect them, how you will feel if you're the victim yourself, what are the consequences you will face, and how will this small little act affect your profile as well as your family and friends. Then, do; after thinking through, make your decision and act as you wish. The final decision will still be in your hands, whether to steal or to leave.
Bullying
Bullying is getting more serious in this society and especially in Singapore, with up to 1 in 5 youths being bullied in school. For this section of the equipping workshop, each team was given 10 minutes to illustrate anything about bullying, be it the forms of bullying, the consequences, the effects, the feelings. TK brainstormed and planned a little, and after 10 minutes :

The red line in the middlle shows the emotional part, where victims feel horrible and bullies feeling high.
Basically bullying can be classified into various categories being : Verbal bullying, Physical bullying, Relational bullying and Cyber bullying. Many do not realise that by simply calling people names or poking others or telling your friends not to befriend someone else or threatening or blackmailing, it is actually considered bullying. It is these little little things that accumulate in the heart that in the end cause so much tenson that result in victims harming themselves physcially. I believe there're many reported cases seen, like teens slashing their wrist to vent out the pain inside them. Some even resort to committing suicide after bearing the pain for years.
Most victims bear the pain inside them because of their low self-esteem. And because they are being bullied, they have even lesser confidence in themselves, therefore they are less likely to let anyone know that they're being bullied.
So as a magnanimous Samaritan or just an ordinary individual, i hope that you'll help anyone who's in trouble to face reality and overcome any obstacles. This is a little something we can all do with our little strength to make a big difference in the society.
. . . . .
Saturday, 1 September 2007
This very special dayY
They taught me to be a better peron, to lead, to serve, to see things from all angles, to set my priorities right; they nurtured me to believe in myself, believe in what in what I still believe is the most important in my life - LIFE VALUES. They believed in me and I never once let them down.
It gets emotional every time when I think about how much a difference all of them have made in my life; Mrs Yew (then Miss Kong) for helping me in adapting to school life, Ling Lao Shi for making Chinese Language my friend, Wang Mei De Lao Shi for making Chinese lessons come alive and pulling my standard even higher and also intoducing me to Chinese Calligraphy; Mrs Pang for giving me my 1st leadership position in my life; Mrs Ng for introducing Bhangra into my life and got me involved in performing arts and recognising me as a potential dancer; Miss Liew for teaching English Grammar rules all over again though we were already in P6 and slowing down the pace of teaching for Mathematics just to ensure that the concepts got into our heads; Mr Rahmat for hearing out those thoughts and a great friend indeed and also seeing leadership potential in me as the then Prefect Master; Mr Chee for being another great friend... ... ... ... ... and the list just goes on and on
Well, there's another group of educators whom I want to thank too- My Family.
Regardless of how severe or silly a mistake I've made, they were always there for me. They don't really know how to express that love and care physically or anythg that can be seen, but I know that the love and care still exist spiritually. For all the talks DaJie gave me and all the lectures I attended by JinJin KorKor and WeiWei KorKor, I've truely learnt a lot and grown much more and I'm proud to call every single one of you at home a family member of mine. For you have engraved rich values in me over the years.
For 1 thing which all of them gave me was simply trust and believe.
For believing in me, you have all created the confidence in myself to project myself in the public, to be out-spoken, to be interactive and socialable, to think about others, to share my knowledge with others, to help anyone in anyway, to think positively, to lead a meaningful and fruitful life, and most of all, be like them if possible- to touch others and hopefully make a difference in their lives.
. . . . .
littlest of the Pang Family
people call me ChiawMIN or ZhaoMIN
was from Maha Bodhi School
and TanjongKatongSEC
and Temasek Polytechnic
Temasek Design School
tracking people
PANGsters
大哥
二哥
know littlest PUNK even better
HANrelated
MeiFen
MAHA BODHIANS
Alwin
Dennis
LiXin
Michelle
Moyra
TzeChong
YingTing
YingXin
TKsians
Alicia
Amelia
Asha
Atiqah
BoonYee
Celine
Charmaine
Clarissa
Dean
Desiree
Eileen
Erina
EstherTay
EugeneKay
EvelynChan
Farhan NomborSatu
FarisFarizuan
Hafiz
Hasif
HuiMin
HuiJun
HuiXun
James
Janice
JasmineKok
JasminePoh
JiaJun
JinFei
Jolene
Josephine
JovanYo
JunHui
Kane
Kenneth
Mark
Michelle
MingJie
Nazri
NicholasAw
Nigel
Nikki
Novia
PohKing
Rifat
Rohaida
Ryan
SandyLikitdachavongs
Sara
Sharmane
Sharon
SiHui
SiYan
SiYuan
SooHan
Stefan
WeiLin
WeiYing
YinShuang
YongJia
Xenia
Yuyi
ZhangXin
NgeeAnnSec
ChinaExchange'07
Pamela
SherylChia
Shimei
TzeChong
ZhongHuaSec
ChinaExchange'07
ChiehLing
Grace
Stella
them
TK3J'08cum4J'09
Crystal
KelvinPang
WeiYing
YanYing aka YY
YeeJia
YuJia
other STUDENT LEADERS
JonothanSeng/HwaChongInsttn
JoelLim/MarisStella
ShaunSeah/MarisStella
Jesmine/TKGS
CherylSeah/PLMGSS
EleanorNeo/PLMGSS
Hannah/PLMGSS
Joanne/PLMGSS
WeiKee/PLMGSS
ZiQi/PLMGSS
September 2007
October 2007
November 2007
December 2007
January 2008
February 2008
March 2008
April 2008
May 2008
June 2008
July 2008
August 2008
September 2008
October 2008
November 2008
January 2009
February 2009
March 2009
April 2009
May 2009
June 2009
July 2009
August 2009
September 2009
November 2009
December 2009
January 2010
February 2010
March 2010
April 2010
May 2010
June 2010
July 2010
August 2010
September 2010
October 2010
November 2010
January 2011
February 2011
June 2011
July 2011
Layout - Novemrain
Hosting - Blogger
Image - DeviantArt
